Starting a business is an exciting challenge. You probably have a great idea, but how do you bring it to life? Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is one of the smartest ways to test your idea without spending a lot of time or money. This article explains what an MVP is, why it’s essential for startups, and how you can create one step by step.
MVP development for startups means creating a basic version of your product with essential features. It helps test your idea, gather feedback, and make improvements without spending too much time or money. Start small, stay focused, and build what your users truly need.
Now let’s explore how to refine your MVP based on user feedback and take the next steps toward growth.
Checklist
What Is an MVP?
An MVP, or Minimum Viable Product, is the simplest version of your product that solves a core problem for users. It includes only essential features and helps you test your idea quickly without spending too much time or money. The goal is to gather feedback and understand user needs before committing to building the full product.
An MVP focuses on solving a specific problem with minimal resources. Startups and businesses use it to validate ideas early and make smarter decisions. Instead of creating every possible feature, you focus on what matters most to your users. This approach saves time, reduces risks, and provides valuable user insights.
MVPs allow businesses to test their assumptions. For example, instead of assuming users need a feature, you build the MVP to see their actual reaction. This process helps businesses understand what works, what doesn’t, and what needs improvement. It also highlights opportunities for growth based on real-world feedback.
A great example of an MVP is Dropbox’s early days. Instead of developing the entire product upfront, the creators made a simple video demonstrating the concept. This helped gauge user interest and validate the idea without significant investment. Based on the feedback, they built a basic version of the product, which eventually grew into the platform we know today.
Why Is an MVP Important for Startups?
An MVP, or Minimum Viable Product, lets startups test their ideas quickly and affordably. By focusing only on the most essential features, it helps businesses understand if their product meets user needs. This approach saves time, reduces risks, and guides smarter decisions during development.
Here are the benefits of an MVP for startups:
- Saves Money: Building an MVP costs less than creating a full product. By avoiding extra features, startups can validate ideas without overspending.
- Speeds Up Launches: An MVP allows you to bring your product to market faster. A quicker launch helps you test how users react earlier in the process.
- Reduces Risk: Startups can avoid major setbacks by using an MVP to see if their idea actually works. This limits the chances of making costly mistakes.
- Collects Essential Feedback: MVP users offer valuable opinions. Their feedback shows you what works, what doesn’t, and what your product needs.
- Improves Focus: An MVP forces startups to prioritize the most important features. This focus ensures that initial development goes toward solving the user’s main problem.
- Attracts Investors: A working MVP shows potential. It’s proof that your idea has demand. This makes convincing investors much easier.
An MVP is a practical way for startups to bring ideas to life while minimizing risks. It lets you learn from real users and improve your product step by step. With its cost-effectiveness and focus on user needs, an MVP ensures startups stay efficient and better prepared for success.
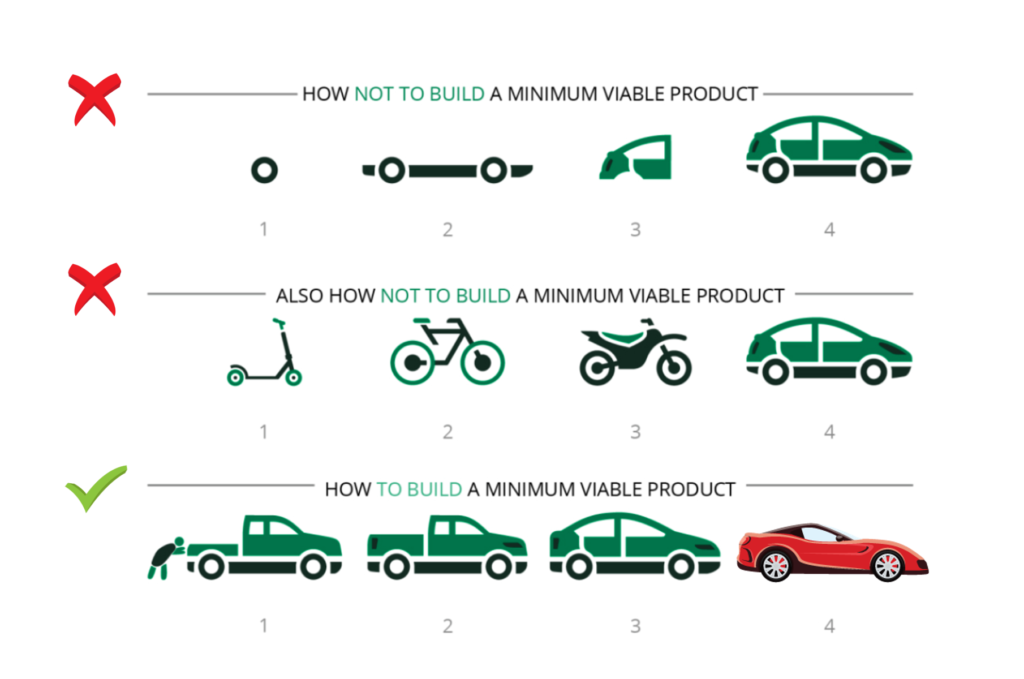
5 Steps to Build an MVP
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a strategic way for startups to test ideas and minimize risks. By focusing on core features, you can deliver value to users quickly and gather meaningful feedback.
Here’s a detailed guide on the key steps to create an MVP and set the foundation for future success.
Step 1: Identify the Core Problem
Every successful product starts with solving a clear problem. Before you create anything, take the time to define the core issue your product will address. This involves understanding your target audience’s pain points and figuring out what they truly need. Conduct surveys, interviews, or market research to gather real-world insights.
Once you pinpoint the problem, ensure it’s specific and solvable. A well-defined problem lays the groundwork for a focused MVP. Remember, trying to solve too many issues at once will dilute your efforts. By concentrating on one clear problem, you not only simplify development but also increase the chances of connecting with your audience.
Step 2: Prioritize What Matters
After identifying the problem, list the features that could potentially solve it. Then, filter this down based on what’s most critical. Focus on the minimum features required to deliver value to your users. This stage is about cutting out unnecessary complexity and letting the main functionality shine.
Create a hierarchy of features. Rank them based on their importance and impact on solving the user’s problem. For example, if you’re building a fitness app, tracking workouts might be essential, while adding personalized tips can wait. Prioritization ensures you allocate resources effectively and build a product users can quickly connect with.
Step 3: Prototyping and Testing
Once the key features are clear, it’s time to develop a prototype. A prototype is a basic version of your product that visually represents how it will work. It doesn’t have to be perfect, but it should convey your concept in a tangible way. Sketches, clickable wireframes, or interactive mockups are common prototyping tools you can use.
Testing your prototype is crucial. Share it with potential users, team members, or stakeholders to gather feedback. Ask them if the product solves their core problem and note any areas of confusion. The insights you gain at this stage help refine your idea before moving into full development.
Step 4: Launch Quickly, Learning Continuously
The next step is to build and launch the MVP. At this stage, you take your prototype and develop a working version with the minimum viable features. Use simple tools and technology to keep development costs low and timelines short. Don’t focus on creating a perfect product—focus on delivering functionality.
Once your MVP is ready, release it to a controlled group of users like early adopters or beta testers. Observe how they interact with your product, and collect feedback systematically. This feedback loop is vital. It helps you understand what resonates with users and where adjustments are needed.
Step 5: Iterate and Grow
Building an MVP is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. After launching your MVP and collecting feedback, you’ll identify areas for improvement. Maybe users want an additional feature or find a certain aspect of the product difficult to use. Using this feedback, start iterating—refine existing features, add new ones strategically, and enhance the overall experience.
Growth happens when you consistently learn from your users and adapt. Use data, such as usage patterns or survey results, to guide your decisions. Over time, these iterative improvements transform your MVP into a full-scale product that meets user demands and thrives in the market.
Building an MVP is a smart and practical way to test ideas, learn from users, and grow strategically. Starting with a well-defined problem, prioritizing essential features, and focusing on feedback ensures you stay aligned with user needs. By following these steps, your MVP can become the stepping stone to a successful and impactful product. Start small, listen closely, and keep improving!
Mistakes to Avoid in MVP Development
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a powerful way to test ideas and discover what users truly need. When done right, it helps startups save time, money, and resources. However, common mistakes can derail your efforts.
Below are the key mistakes to avoid, along with simple actions to keep your MVP process on track.
- Adding Too Many Features: Including too many features makes your MVP complex and slow. Stay focused on solving one core problem to keep things simple and clear.
- Skipping User Feedback: Missing user feedback means missing real improvements. Listen and adjust based on what users need.
- Taking Too Long to Launch: Waiting too long hurts your MVP’s growth. Launch quickly, then learn and improve with real user feedback.
- Not Testing Enough: Test your MVP with a small group to spot issues early. This helps fix problems before reaching more users.
- Losing Focus on the Core Problem: Extra features distract from solving your main problem. Keep the MVP centered on what users need most.
- Ignoring Market Research: Skipping market research means missing what your audience wants. Learn their needs early to shape a product that fits.
- Poor Communication with the Team: Clear communication keeps everyone working toward the same MVP goals. Misaligned teams waste time and build the wrong features.
- Relying Too Much on Technology: Too much focus on tech can make your MVP hard to use. Balance features and design with simple, user-friendly solutions.
- Launching Without Clear Goals: Set clear objectives for your MVP. Knowing your goals keeps efforts focused and avoids wasting resources.
- Not Planning Iteration: Treat your MVP as the first version, not the finished product. Plan for regular updates and improvements using user feedback.
Developing an MVP is more than just minimizing features—it’s about staying focused, gathering feedback, and continuously improving. Avoid these common mistakes to maximize your chances of creating a product that resonates with users. Build simple, prioritize learning, and approach your MVP as the first step toward lasting success.
Final Thoughts
An MVP, or Minimum Viable Product, is a smart way to bring ideas to life efficiently. It allows you to start small and focus on delivering value without overwhelming resources. By testing a simplified version of your product, you can learn what matters to users and adjust based on their needs. This process not only reduces risks but also ensures that every step forward is informed by real-world feedback.
One of the greatest strengths of an MVP is its ability to validate your concept early on. Instead of guessing what features users want, you put a basic product in their hands and gather their reactions. This approach saves you from wasting time and money on elements they don’t care about. Focusing on core problems and essential features during development builds trust with users and helps you grow in a meaningful, targeted way.
MVP development is also a foundation for long-term success. Through continuous testing and iteration, your product evolves to meet user needs more effectively. This method ensures that your final product is robust and solves real problems. By starting with an MVP mindset—testing, learning, and improving—you’re not just building a product; you’re building a solution that endures.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is an MVP in product development?
An MVP is the smallest version of a product with key features to solve a main problem. It helps test the idea quickly and affordably. - Why is an MVP important for startups?
An MVP is important for startups because it saves time, cuts costs, and reduces risks. It validates ideas with real users. - How does an MVP help save money?
An MVP avoids unnecessary features and focuses only on essentials. This reduces development costs and avoids wasted resources. - What is the first step to building an MVP?
The first step to building an MVP is identifying the core problem. Products succeed when they solve a specific issue. - How are features prioritized for an MVP?
Features are prioritized by focusing on solving the core problem first. Non-essential features can wait for later versions. - What is the role of feedback in MVP development?
Feedback is crucial in MVP development as it shows what works and what doesn’t. Improvements rely on user input. - How does testing improve an MVP?
Testing improves an MVP by finding flaws, fixing bugs, and ensuring usability. Testing ensures the product works as intended. - What are common mistakes in MVP development?
Common mistakes include adding too many features, skipping feedback, launching too late, and poor testing. Focus and testing prevent these. - What is an example of a successful MVP?
Pathao started with a simple bike-sharing service. It solved local transportation problems and then expanded services based on needs. - How can iteration improve an MVP?
Iteration improves an MVP by incorporating user feedback. Constant updates ensure the product stays relevant and effective.

